-
Posted By admin
-
-
Comments 0
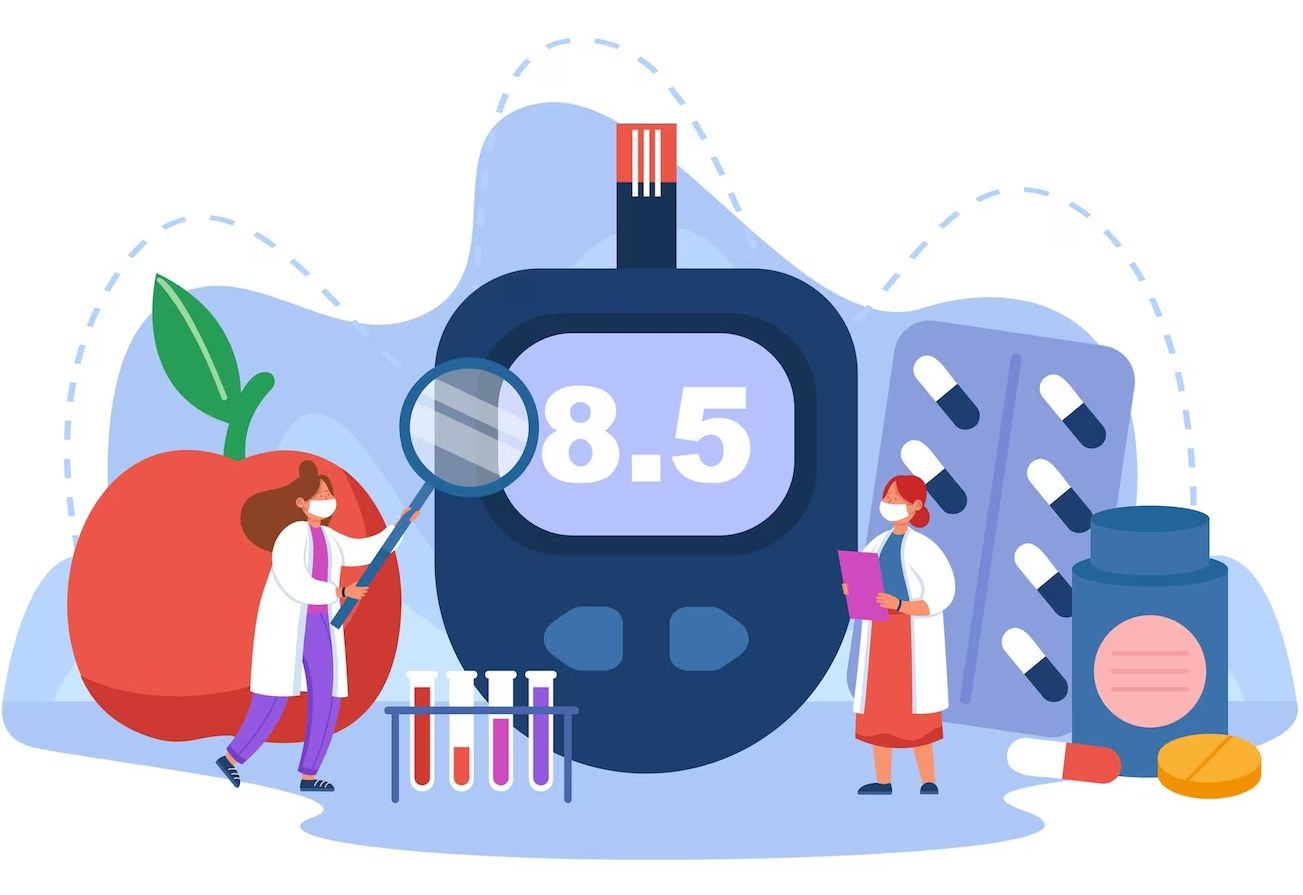
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar, or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which can cause a range of health complications if not managed properly. In this article, we will delve into the various types of diabetes, their causes, and strategies for effective management.
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in a complete lack of insulin, necessitating regular insulin injections to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age.
- Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for around 90-95% of all cases. It primarily affects adults, though it can develop in children and adolescents. In type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, and the pancreas may not produce enough insulin to compensate. Lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity contribute significantly to its development.
- Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands. This condition typically resolves after giving birth, but women who have had gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Diabetes
- Genetic Predisposition
A family history of diabetes can increase an individual’s risk of developing the condition. While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices also significantly influence the likelihood of developing diabetes.
- Insulin Resistance
In type 2 diabetes, cells in the body become less responsive to insulin, making it harder for glucose to enter cells. This results in elevated blood sugar levels.
- Autoimmune Response
In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is still under study, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to be involved.
- Hormonal Changes
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can lead to gestational diabetes. These hormonal shifts can affect insulin sensitivity, making it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar levels.
Management and Treatment
- Medication
For type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is crucial and often requires multiple daily injections or the use of an insulin pump. Type 2 diabetes may be managed through oral medications that improve insulin sensitivity, injections that stimulate insulin production, or a combination of both.
- Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing all types of diabetes. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes. This can be done using a blood glucose meter at home or through continuous glucose monitoring systems.
- Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring the progression of diabetes and addressing any complications that may arise.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires lifelong management. Understanding the different types, their causes, and how to effectively manage them is crucial for individuals living with diabetes. With proper medical care, a healthy lifestyle, and support, individuals with diabetes can lead full and active lives while minimizing the risk of complications. Remember, early detection and proactive management are key to maintaining good health for those with diabetes.